Farming remarks
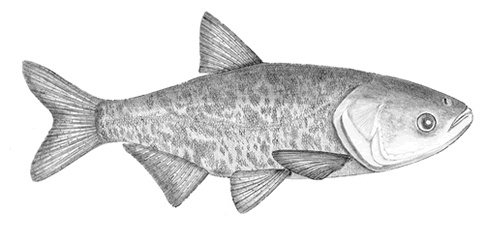
Hypophthalmichthys nobilis is one of the four Chinese major carps, together with H. molitrix, Ctenopharyngodon idella and Mylopharyngodon piceus. H. nobilis is a native freshwater fish from lakes, rivers, and reservoirs of south and central China, but has already been introduced in many countries. This eurythermic carp dwells in the upper layer of the water column, being considered a planktivorous fish – especially feeding on zooplankton – but it can also feed on detritus and BENTHIC organisms on the bottom opportunistically. It is one important aquaculture species that has been farmed for more than a thousand years and, together with H. molitrix, is one of the most intensively cultured fish species in Asia. H. nobilis is frequently used as a filter-feeding fish in polyculture ponds in China, stocked for water quality improvement and as a biocontrol method for phytoplankton. Besides ponds, this carp is also commonly raised in pens, cages or reservoirs with other carps or other fish species as Ictalurus punctatus and Polyodon spathula. A competition for food may be expected with Labeo catla or with other FISHES with similar feeding habits in such polycultures. It is a fast growing fish that can be sold before reaching maturity. In natural conditions, this carp migrates to the upper reaches of rivers to spawn during early summer, with rising water level as the essential stimulus for this. Despite its commercial importance, most wild information is still missing for this species. After being harvested, very little handling and processing is used with this fish, as it is usually consumed fresh, mainly locally. Further research about the slaughtering process is needed as well as about substrate use, stress response, and malformations under farming conditions.
Note: The age class "Adults" for farming conditions refers to large juveniles and young adults due to farmers estimating age class by size rather than by maturity status. Also, “Adults” refers to individuals to become spawners or for algae control, as the literature does not always specify.
For details see: WelfareCheck | farm